
HL Paper 1
What is the correct explanation for the colour of [Cu(H2O)6]2+?
A. Light is absorbed when an electron moves to a d orbital of higher energy.
B. Light is released when an electron moves to a d orbital of higher energy.
C. Light is absorbed when electrons move from the ligands to the central metal ion.
D. Light is absorbed when electrons move between d and s orbitals.
What is the charge on the iron(III) complex ion in [Fe(OH)2(H2O)4]Br?
A. 0
B. 1+
C. 2+
D. 3+
The oxidation state of cobalt in the complex ion [Co(NH3)5Br]x is +3. Which of the following statements are correct?
I. The overall charge, x, of the complex ion is 2+.
II. The complex ion is octahedral.
III. The cobalt(III) ion has a half-filled d-subshell.
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
[CoCl6]3– is orange while [Co(NH3)6]3+ is yellow. Which statement is correct?
A. [CoCl6]3– absorbs orange light.
B. The oxidation state of cobalt is different in each complex.
C. The different colours are due to the different charges on the complex.
D. The different ligands cause different splitting in the 3d orbitals.
Which of these statements are correct?
I. Zinc is not a transition element.
II. Ligands are Lewis bases.
III. Manganese(II) chloride is paramagnetic.
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Which of these ions are likely to be paramagnetic?
I. Ti3+
II. Cr3+
III. Fe3+
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
What is the overall charge, , of the chromium (III) complex?
A. 0
B. 1+
C. 2−
D. 3+
What is the oxidation state of the metal ion and charge of the complex ion in [Co(NH3)4Cl2]Cl?
Which electrons are removed from iron (Z = 26) to form iron(II)?
A. two 3d electrons
B. two 4s electrons
C. one 4s electron and one 3d electron
D. two 4p electrons
Which factor does not affect the colour of a complex ion?
A. temperature of the solution
B. identity of the ligand
C. identity of the metal
D. oxidation number of the metal
What is the effect of a stronger ligand?
Which is correct for the complex ion in [Fe(H2O)5Cl]SO4?
Why is hydrated copper (II) sulfate blue?
A. Blue light is emitted when electrons return to lower d-orbitals.
B. Light complimentary to blue is absorbed when electrons return to lower d-orbitals.
C. Blue light is emitted when electrons are promoted between d-orbitals.
D. Light complimentary to blue is absorbed when electrons are promoted between d-orbitals.
[Cr(OH2)6]3+ is violet and [Cr(NH3)6]3+ is yellow. What is correct?
The Colour Wheel
Which complex has the greatest d orbital splitting?
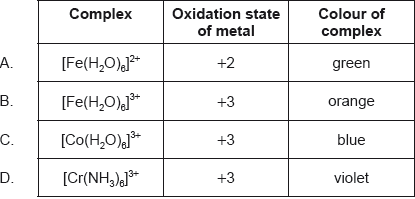
Which complex ion contains a central ion with an oxidation state of +3?
A. [PtCl6]2−
B. [Cu(H2O)4(OH)2]
C. [Ni(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+
D. [Co(NH3)4Cl2]+
Ammonia is a stronger ligand than water. Which is correct when concentrated aqueous ammonia solution is added to dilute aqueous copper(II) sulfate solution?
A. The d-orbitals in the copper ion split.
B. There is a smaller splitting of the d-orbitals.
C. Ammonia replaces water as a ligand.
D. The colour of the solution fades.
How is colour produced in transition metal complexes?
A. Light is absorbed when electrons are promoted between split d-orbitals.
B. Light is emitted when electrons fall between split d-orbitals.
C. Light is absorbed when electrons escape from the complex.
D. Light is emitted when the complex returns to ground state.
Part of the spectrochemical series is shown for transition metal complexes.
I−< Cl− < H2O < NH3
Which statement can be correctly deduced from the series?
A. H2O increases the p–d separation more than Cl−.
B. H2O increases the d–d separation more than Cl−.
C. A complex with Cl− is more likely to be blue than that with NH3.
D. Complexes with water are always blue.