Types of organization charts
To recap your understanding of types of organizations, review this video:
ATL Activity 1 - School organization structure

Investigate the organizational structure at your school. Construct as accurate of an organizational chart as possible for your school.
Typically, an IB World School will include a senior management / leadership team consisting of:
a principal (head teacher / administrator)
vice principals (deputy head teachers in charge of different strategic aspects of the school, such as the curriculum, pastoral care, and staff professional development)
business managers (in charge of non-teaching and financial aspects of the school)
The rest of the school's organizational structure will then typically include:
curriculum leaders (such as the IB Coordinator, heads of faculty, heads of department, or subject leaders)
guidance and achievement leaders (such as heads of house, heads of year, or heads of sections)
subject teachers
support staff (non-teaching staff).
Context and culture are important, and each school will be different, so the organizational chart for the school is likely to be quite unique.
ATL Activity 2 (Research and Thinking skills) - Real-world organizational structures
This is a great resource for visual learners, suggested by InThinking subscriber David Weyant - you can search many different real-world organizational charts from different companies, from Adidas and Apple to Vodafone, Walmart, and Zoom here from TheOrg.com
Exam Practice Question - Gene Simons Manufacturer (GSM)

Gene Simons Manufacturer (GSM) is a small producer of plastic toys. In recent years, the business has grown quite significantly so there are now nearly 70 workers. GSM expects the business to keep growing, with almost 100 workers by the end of next year. While demand for plastic toys has fallen in many European markets, GSM is happy that increased disposable incomes in Asia has meant overall sales to toy shops has increased.
However, GSM is concerned that labour productivity in its factory has declined, despite the increased overtime payments made to workers. This is frustrating as GSM has spent a lot of money automating production in its factory. Labour turnover has also increased, so GSM has not been able to benefit from economies of scale.
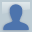
Gene Simons is the chief executive officer (CEO) of the company and has an assistant executive who reports directly to him. There are four directors: Marketing, Human Resources, Production and Accounting. The Marketing Director has three workers who report to her. The Human Resources has 2 people who report to her: the Recruitment and Training Manager, and Remunerations Manager (who is responsible for two other employees). The Production Director oversees the Factory Manager, who controls 50 workers. The Accounts Director is in charge of two staff members.
(a) | Define the term span of control. | [2 marks] |
(b) | State Gene Simon’s direct span of control. | [1 mark] |
(c) | On a separate piece of paper, construct an organization chart for GSM. | [4 marks] |
(d) | From your organization chart, identify the number of levels in the hierarchy at GSM. | [1 mark] |
(e) | Using information in the case study and the organization chart, examine the causes of and solutions to GSM’s labour productivity problem. | [10 marks] |
Answers
(a) Define the term span of control. [2 marks]
The span of control is the number of subordinates that a manager or supervisor directly oversees in the organization.
(b) State Gene Simon’s direct span of control. [1 mark]
One (the assistant executive)
(c) On a separate piece of paper, construct an organization chart for GSM. [4 marks]
.jpg)
(d) From your organization chart, identify the number of levels in the hierarchy at GSM. [1 mark]
Five
(e) Using information in the case study and the organization chart, examine the causes of and solutions to GSM’s labour productivity problem. [10 marks]
Falling labour productivity means that production per worker is decreasing. Gene is also not happy that there are no benefits from economies of scale (as average cost should go down with GSM’s increased scale of production). There could be several reasons for this. The business has increased the number of its workers, yet labour turnover is also increasing and the factory has become more automated. This suggests that workers may not have received adequate training, or the recruitment process could be improved. Furthermore, the factory manager must supervise 50 workers which is perhaps too wide a span of control to be effective. It would be challenging for anyone to manage, coordinate, organize or direct so many workers in order to meet the goals of GSM.
There are solutions. The factory manager needs some assistants to be employed so they can each have a small team to monitor and oversee. This will cost GSM more money but should increase overall productivity. Hiring more managers seems vital as GSM plans to increase production so is likely to hire even more factory workers. Alternatively, GSM could consider introducing more automation rather than employing more workers. This would increase capital spending and existing workers may need retraining. It may help if the Factory Manager works alongside the recruitment and training manager to ensure high calibre workers are recruited and proper training provided, which should increase productivity.
In conclusion, the most important issue is the Factory Manager’s span of control which is too wide. Hence, assistants should be hired who can help to organize and manage the workers. If training and/or recruitment is flawed, this should be rectified quickly, with the involvement of the Factory Manager. Rather than trying to grow the business with falling productivity, Gene Simons should concentrate on fixing what is wrong at the moment.
Top tip: For this type of question, students should identify relevant issues from the case study, use appropriate business management terminology and then make appropriate recommendations.
Download a PDF version of this exam practice question and mark scheme here.
This exam practice question has been reproduced with the kind permission of Level7 Education Limited
Key terms
A flat organization (also known as a horizontal structure) has only a few layers of management in its organizational structure.
Hierarchical organizational structures are tall/vertical, with many levels in terms of ranks.
An organizational chart is a diagrammatic representation of an organization’s formal organizational structure.
A tall organization (also known as a vertical structure) has many layers in its organizational hierarchy.
Organization by function means structuring a workforce according business functions, i.e. specialised roles or tasks.
Organization by product means structuring a workforce according to the goods or services sold.
Organization by region means structuring a workforce according to different geographical areas based on where the firm’s operations are.
Return to the Unit 2.2 Organizational structure homepage
Return to the Unit 2 Human resource management homepage
 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team







.jpg)