Unit 2.8(2): Market failure - merit goods and demerit goods
Merit goods, demerit goods and public goods are all associated with significant market failure. When this happens there is an important role for state intervention to correct these market failures. The concepts of merit, demerit goods and public goods were developed extensively by Professor Richard Musgrave (UCLA).

- Theory of merit goods
- Under-consumption of merit goods as a market failure
- Theory of demerit goods
- Over-consumption of demerit goods as a market failure
Revision material
 The link to the attached pdf is revision material from Unit 2.8(2): Market failure - merit goods and demerit goods. The revision material can be downloaded as a student handout.
The link to the attached pdf is revision material from Unit 2.8(2): Market failure - merit goods and demerit goods. The revision material can be downloaded as a student handout.
Introduction

Merit goods, demerit goods and public goods are all associated with significant market failure. When this happens there is an important role for state intervention to correct these market failures. The concepts of merit, demerit goods and public goods were developed extensively by Professor Richard Musgrave (UCLA). His analysis of these goods are examples of why governments need to intervene in certain markets.
Merit goods
What is a merit good?
Merit goods are goods that society says people should consume because they are associated with significant social benefits. Merit goods are a normative concept because they are based on a society’s judgement of what is or is not a merit good.
Examples of merit goods
Deciding what is or what is not a merit good is not that easy. Most textbooks focus on goods and services associated with health and education as merit goods and their provision is supported by most governments across the world. This can be broadened to include things like healthy food, recreation facilities, housing, museums and theatres. Where the examples of merit goods stop is difficult to say precisely and their existence is often influenced by political decision-making by governments.
Merit g oods are an example of market failure because they tend to be under-consumed in free markets and this leads to an under-allocation of resources. Merit goods are often associated with significant external benefits to society from their consumption, and these are not accounted for in the free market allocation of resources.
oods are an example of market failure because they tend to be under-consumed in free markets and this leads to an under-allocation of resources. Merit goods are often associated with significant external benefits to society from their consumption, and these are not accounted for in the free market allocation of resources.
School education is a good example of how there would be under-consumption of a merit good in a free market without any government intervention. Remember, in the free-market model of the economy there would be no government-funded and managed state schools.
There are three aspects to the under-consumption school education:
External benefits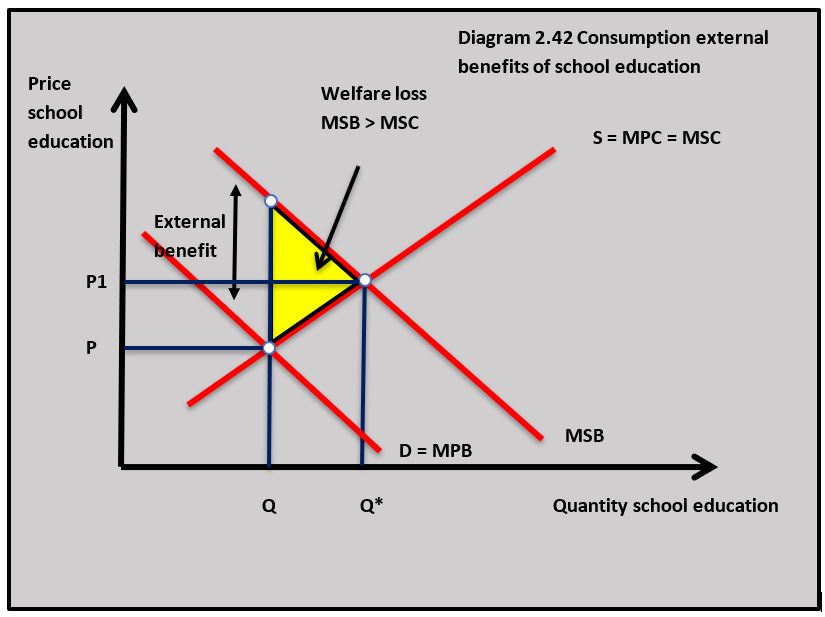
When people are deciding to send their children to school, they do not consider the external benefits of school education. There are significant positive externalities associated with children attending school: they provide a more skilled workforce; they learn social skills that make them better citizens and they are likely to be healthier because they are taught how to live healthy lives. Diagram 2.42 illustrates the under-consumption of school education and its associated welfare loss.
Undervalued private benefits
Individuals make buying decisions based on their assessment of the private benefits the consumption of a good will give to them. People often under-value the benefits the consumption of a merit good will bring to them. Many people in society will value the education of their children very highly and will always send their children to school. Some people, however, might not see such a high value in education and would not be willing to pay for their children to go to school.
Low incomes households
School education is expensive, and some people would not be able to afford to send their children to school in a free market situation. The children of low-income households will miss out on the significant private benefits of attending school and society will not benefit from the positive externalities of educating the children of low-income households.
Dr Ben.jpg) g Goh is a consultant physician at Royal London Hospital discusses the use of face masks to protect the population from Covid-19. He argues that as people use face masks together with social distancing and hand-washing, this will significantly reduce the transmission of coronavirus and saves people’s lives. France is the latest country to advise the use of face masks along with the US, Austria and Singapore. Covid-19 is often spread when tiny viral particles people breathe in crowded places like trains and buses. Masks are seen as an important way of preventing this. Masks protect those wearing them from contracting Covid-19 and they also protect third parties from contracting the infection as well.
g Goh is a consultant physician at Royal London Hospital discusses the use of face masks to protect the population from Covid-19. He argues that as people use face masks together with social distancing and hand-washing, this will significantly reduce the transmission of coronavirus and saves people’s lives. France is the latest country to advise the use of face masks along with the US, Austria and Singapore. Covid-19 is often spread when tiny viral particles people breathe in crowded places like trains and buses. Masks are seen as an important way of preventing this. Masks protect those wearing them from contracting Covid-19 and they also protect third parties from contracting the infection as well.
 Worksheet questions
Worksheet questions
Questions
a. Define the term merit good. [2]
Merit goods are goods that society says people should consume because they are associated with significant social benefits.
b. Explain why merit goods are an example of normative economics. [4]
Merit goods are an example of normative economics because they represent a judgement of what people should or ought to consume. Governments encourage the consumption of merit goods because they believe they will be good for society.
c. Explain two reasons why merit goods such as face masks might be under-provided in a free market economy. [4]
The first reason is that face masks are associated with positive externalities and the external benefits of face masks will not part of the demand curve in the market. The second reason is some consumers will choose not to wear masks out of their personal preference and will not think about the medical benefits of wearing one. These two reasons mean the socially efficient output of wearing masks will be greater than the market output.
d. Using a diagram, explain why merit goods are under-consumed in a free market. [4]
 Because of the positive externalities associated with face masks, the market output in the diagram (MPB equals MPC) at Q is below the socially efficient output (MSB equals MSC) at Q*.
Because of the positive externalities associated with face masks, the market output in the diagram (MPB equals MPC) at Q is below the socially efficient output (MSB equals MSC) at Q*.
Investigation
Research into other examples of merit goods related to the Covid-19 crisis?
Demerit goods
What is a demerit good?
Demerit goods are goods that society says people should not consume because their consumption is associated with significant social costs. Like merit goods, demerit goods are a normative economic concept and are based on a society’s judgement of whether the consumption of a good should be discouraged.
Examples of demerit goods
Commonly used examples of demerit goods include alcohol, cigarettes, firearms and recreational drugs. But these examples can be extended to violent films, ownership of dangerous animals, junk food and gambling. As with merit goods, the distinction of what is or is not a demerit good depends on where you are in the world and the political and cultural values of a country.
Demerit goods as a market failure
Demerit goods are an example of market failure because they tend to be over-consumed in free markets. Without any state intervention in a free market, there will be an over-allocation of resources. One of the key reasons for this is that demerit goods are associated with negative externalities.
Alcohol is an example where there is over-consumption in a free market. Its over-consumption can be explained in two ways:
External costs
There is considerable evidence to show that the consumption of alcohol leads to negative externalities that adversely affect others in the form of poor behaviour by individuals in public places; drink driving; absenteeism and low level of productivity at work and domestic violence. In addition, people who consume large quantities of alcohol often use the healthcare system excessively and this reduces its availability to others.
 Diagram 2.43 shows how the over-consumption of alcohol and the associated welfare loss.
Diagram 2.43 shows how the over-consumption of alcohol and the associated welfare loss.
Overvalued private benefits
Demerit goods like alcohol are also over-consumed because people do not consider the impact on their long-term welfare when consuming it. When individuals drink too much alcohol over a long period of time they might not factor in the impact it has on their physical and mental health.
 10 teenagers were taken into custody by the Police in the western Indian state of Gujarat for playing the online video game PlayerUnknown’s Battlegrounds (PUBG) a game related to the popular game Fortnite. The ban on PUGB was recently introduced by local governments in India to deal with ‘violent traits’ in young people who play it.
10 teenagers were taken into custody by the Police in the western Indian state of Gujarat for playing the online video game PlayerUnknown’s Battlegrounds (PUBG) a game related to the popular game Fortnite. The ban on PUGB was recently introduced by local governments in India to deal with ‘violent traits’ in young people who play it.
A local police commander said, “Due to these games, the education of children and youth are being affected and it affects the behaviour, manners, speech and development of the youth and children.”
PUBG is marketed by the South Korean firm Bluehole and is a survival-themed battle game that puts online players on an island where they try to eliminate each other.
 Worksheet questions
Worksheet questions
Question
Explain why demerit goods might lead to market failure. [10]
Answers should include:
- Definitions of demerit goods, market failure and negative externalities.
- A diagram to show the over-consumption of a demerit good like a violent video game. In the diagram shown the market output is at Q which is above the socially efficient output at Q*.
- An explanation that the negative externalities of consumption associated with violent video games mean the MSB is below the demand curve. This means the market output where MPB equals MPC is above the socially efficient output where MSB equals MSC.
- The yellow shaded area is the welfare loss associated with the consumption of violent video games.
- Answers should include examples of the external costs of violent video games like possible increased violent behaviour in society.
- There should also be an explanation that buyers of violent video games may not think about their long-term welfare.
Investigate other video games that people have wanted to be banned. Think about them in terms of their external costs and as demerit goods.
When individuals are making choices about the goods and services they buy they are generally free to choose what they want. Classical economic theory considers the choices consumers make on the principle that individuals aim to maximise their utility from their available income. The theory of merit and demerit goods raises interesting questions about whether consumers make choices that maximise their satisfaction in the long run. If someone chooses to smoke or vape it might maximise their utility at that moment but what about their utility in 20 years when they have a constant cough and breathing difficulties. It is also interesting to consider the extent to which people make consumption choices about their utility relative to community welfare.
To what extent do people get vaccinated for themselves or are they thinking about the wider benefits for society?
Which of the following statements is the best definition of a merit good?
Which of the following best explains why demerit goods are over-consumed in a market?
Individuals may not take into account the negative consequences to themselves of consuming demerit goods like alcohol.
Which of the following is the best example of a demerit good?
Vaping is the best example because it is the most regulated by the government because of the judgement it makes about the risks of consumption.
Which of the following is not true about the diagram showing the market for cigarettes?

Cigarettes are being over-consumed as a demerit good.
Which of the following is least likely to be an example of a merit good?
Personal computers are associated with social benefits but the other options are stronger examples.
Which of the following is most likely to be true of a merit good?
Consumers often undervalue the private benefits they might receive from a merit good like healthcare or education.
Which of the following is most likely to be a characteristic of a merit good?
Because of positive externalities of consumption merit goods are often under-provided.
Recreational drugs are most likely considered to be a market failure because?
The negative consumption externalities associated with recreational drugs means their marginal social cost is greater than the marginal social benefit at the market equilibrium.
Which of the following is the most important characteristic of merit goods?
Merit goods are often under-consumed because they are associated with positive externalities of consumption.
Which of the following is the most important characteristic of demerit goods?
Demerit goods are often over-consumed because they are associated with negative externalities of consumption.
 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team
